Lewis Diagrams and Chemical Reactions

Learning Intentions
- To learn how to use Lewis diagrams to represent ions
- To learn different ways of representing the same chemical reaction
Notes
Open the Ionic and Covalent Bonding Simulation from the American Association of Chemistry Teachers.
Create a compound with an ionic bond.
Create a compound with a covalent bond.
- Create a compound consisting of only one element.
Class Questions
Using the Internet, answer the following questions. We will go over the answers in class.
- In a Lewis diagram, what do each of the following represent?
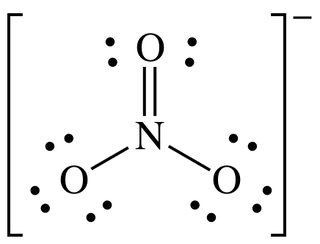
- A dot
- A single line
- A double line
- A triple line
- A chemical symbol
- Square brackets
- A number, plus sign, or minus sign in superscript above square brackets
- Define the following terms:
- Valence electron
- Ionic bond
- Covalent bond
- Acid
- Base
- Salt
- Neutralization reaction
- Cation
- Anion
- Polyatomic ion
- Diatomic element
- How do you know if a compound has ionic or covalent bonds?
- How do you create the name for an ionic compound?
- How do you create the name for a covalent compound?
- What are the 7 diatomic elements?
- What do the following subscripts mean in a chemical equation?
- (s)
- (l)
- (g)
- (aq)
- What is the formula and ionic charge of the following polyatomic ions?
- Ammonium
- Nitrite
- Nitrate
- Sulfite
- Sulfate
- Hydrogen sulfate (a.k.a. bisulfate)
- Hydroxide
- Phosphite
- Phosphate
- Hydrogren Phosphate
- Perchlorate
- Chlorite
- Chlorate
- Acetate
- Carbonate
- Hydrogen carbone (bicarbonate)
- Peroxide
- Cyanide
Partner Questions
With your partner, for each of the following
chemical reactions,
- Write out the balanced chemical reaction (include subscripts showing the state).
- Draw out the Lewis diagrams of the products and reactants.
- Describe the type of reaction.
- Oxygen gas rusts solid iron to produce solid iron (III) oxide.
- Solid potassium reacts with liquid water to produce aqueous potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
- Electricity is passed through liquid water to produce hydrogen gas and oxygen gas.
- Aqueous sodium hydroxide reacts with aqueous hydrochloric acid to produce aqueous table salt and water
- Aqueous silver nitrate reacts with aqueous table salt to produce solid silver chloride and aqueous sodium nitrate.
- Methane gas (CH4) burns with oxygen gas to produce carbon dioxide gas and water vapour.
